Table of Contents
Introduction 📢
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) represent a transformative technology within digital spaces because they create exclusive ownership rights for digital assets. While Bitcoin and Ethereum function as standard cryptocurrencies users can substitute directly, NFTs represent unique digital assets which cannot be swapped equally for another. NFTs take advantage of blockchain systems which provide security through genuine verification along with unchangeable records and clear trace items.
NFTs enjoy growing popularity because they enable the tokenization of numerous digital and physical objects like art and music as well as virtual buildings and collectibles which allows artists to create new revenue opportunities. NFTs have gained worldwide recognition which generated excitement throughout technological circles as well as other sectors.
NFTs stand at the forefront of ownership transformation because their authentication features together with exclusive digital rights are reshaping operational practices across art market sectors and the gaming plus finance industries. Through NFTs artists gain control by reaching buyers themselves without gallery or auction house intermediaries while receiving secondary market sales revenue.
Players in gaming can now fully own their virtual possessions through NFTs which they can exchange among multiple gaming services to establish new marketplaces within online realms. Through asset tokenization via NFTs the financial industry now offers investors fractional shareholds in valuable commodities along with novel investment methods. Their continued evolution results in an expected expansion of their impact on digital ownership innovation which positions these tokens at the core of contemporary digital economy systems.
What Are NFTs? 👺
NFTs represent tangible assets including artwork and digital videos which have undergone blockchain tokenization processes. Tokens serve as distinctive identifiers because they transform metadata using an encryption function. The tokens secure their position on the blockchain network as the assets remain in separate storage locations. Tokens stay unique because they attach directly to their corresponding assets.
The trade value of NFTs enables transactions involving real currency, other cryptocurrencies and additional NFTs this depends on market value which owners establish for their NFTs. To tokenize real world items through blockchain technology you might draw a smiling graphic onto a piece of fruit then photograph it for metadata purposes before transforming it into blockchain tokens. The individual who controls the private keys to that token holds all of your designated ownership rights.
Cryptocurrencies operate as tokens yet they remain fungible since any two cryptocurrencies from the same blockchain serve as alternatives for one another. Though two NFTs on an identical blockchain might look the same they remain distinct assets and cannot replace each other.
NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) function as online ownership records that define distinct items from various digital material to physical objects. Through blockchain technology NFTs establish a reliable and transparent method to demonstrate authentic ownership of assets like digital artwork, musical compositions, video contents and gaming belongings. Artists can generate an NFT linked to their digital painting which provides buyers ownership of that artwork’s authentic and traceable original version.
Outside of digital applications NFTs represent possession rights of actual items such as real estate properties along with collectables and event passes which establishes a link between the material and digital worlds. This technology enables digital creators to sell their works directly to owners who can trade these assets on decentralized platforms while initiating a fresh ownership model across digital and physical spheres.
History of NFTs ⌛
Although NFTs first appeared in 2014 the digital art market experienced meaningful growth beginning in 2017 due to popular projects such as Rare Pepes and CryptoPunks.
Throughout 2021 NFT interest surged largely because famous personalities such as Snoop Dogg and Paris Hilton endorsed them. At this time both Gucci along with Coca-Cola and Budweiser created their own exclusive NFT collections.
The NFT market tipped upward but later experienced decline in 2022 as over 1.5 million NFTs traded every month demonstrated saturation.
One of the leading organizations in cryptocurrency and Non-Fungible Token operations FTX entered bankruptcy proceedings. Investor losses exceeded $60 million after crypto coins TerraUSD and LUNA erased nearly their entire market value. NFTs faced a dramatic downturn that turned digital assets worthless because fraudulent activities combined with other adverse events throughout the market.
Following its market drop the NFT sector advanced its blockchain infrastructure by enhancing security features as well as operational efficiency. Modern NFT technology now supports not only digital artwork but physical items such as memberships and tickets and extends into virtual spaces including fashion transactions and real estate deals.
How to Create an NFT 🛠️
NFT platforms provide creators with direct access to mint creations while simultaneously enabling blockchain uploads for their artwork. This manual explains how to create your first NFT from artwork uploading through blockchain selection to listing your work for sale.
Many people mistakenly think that the digital file such as an image or video represents the NFT itself. As an actual asset on the blockchain the token represents stored data comprised of hashed details. Another hosting platform like Amazon Web Services keeps the digital item that includes metadata for storage needs. You can save images from NFT auction sites by right-clicking because the image file itself lacks blockchain-verified ownership information. The saved copy you possess lacks the blockchain data which determines NFT ownership so it does not confer ownership to you. You own a duplicated representation at its core.
A token represents hashed item data converted into an alphanumeric string format in this context. In blockchain storage resides the token which certifies ownership of the digital asset.
1) Figure Out What You Want to Create
A NFT is usually connected to digital artwork purposes. A virtual property for NFTs might present as either a visual design, a music track or a brief animated video bite. This process aims to establish digital media that stands alone which buyers can purchase because they resemble traditional works in art galleries.
NFTs create creator value through their singular existence which prevents any other person from taking ownership. Creators must verify ownership of digital content before making an NFT because using someone else’s media to create an NFT invites legal action from the true owner.
2) Choose a Blockchain
Multiple blockchains support the creation process for minting your NFT. The blockchain records permanent transaction history featured in NFT minting demand you select the version which satisfies your individual specifications.
Ethereum
The most popular NFT blockchain is Ethereum, which hosts thousands of NFT collections. Ethereum NFTs are created utilizing the ERC-721 and ERC-1155 standards, which store the metadata of the NFT on the Ethereum blockchain.Most NFT marketplaces support the creation of Ethereum NFTs. Its robust smart contract capabilities further enhance its appeal for intricate NFT projects.
Pros:
- Advanced and versatile smart contracts.
- Large and supportive community.
- Its strong reputation combined with extensive market trust levels supports its operational success.
Cons:
- Network congestion leads to inflated transaction fees maximum.
- Transactions become slower when system demand levels increase.
- Challenges with scalability within the current architecture.
Solana
The nearest competitor to the Ethereum blockchain is Solana. Designed as a faster, lower-cost alternative to Ethereum, Solana offers transaction fees of less than $0.01 and a growing list of supported apps for NFTs.
Pros:
- Swift transaction processing.
- Substantially lower fees compared to many counterparts.
- A burgeoning and supportive ecosystem.
Cons:
- Relatively recent blockchain with less historical data.
- Less decentralised compared to certain other blockchains.
- Occasional network congestion issues.
Bitcoin Ordinals
Bitcoin Ordinals implements a revolutionary protocol network over the Bitcoin blockchain. Ordinals protocol features a new system that supports individual identification and content embedding for each Bitcoin’s smallest unit while allowing it to hold digital data such as audio, visuals and images.
- Unique Identification: Each satoshi is assigned an ordinal number based on its mining order, ensuring unique identification.
- Inscription Capability: Users can inscribe digital content onto individual satoshis, creating a permanent record on the blockchain.
- Taproot Upgrade Utilisation: Bitcoin Ordinals utilise the Taproot upgrade, enabling the inclusion of more complex data in Bitcoin transactions.
3) Set Up an NFT Wallet
The blockchain you select determines which specific digital wallet application you will need to store your NFT. The creation of a wallet requires both downloading a crypto wallet app and entering a username plus password. Important for security management you must keep private keys and recovery phrases stored separately from the wallet using offline storage methods.
There are several popular wallet apps that support multiple blockchains like MetaMask, Coinbase Wallet, Ledger Nano X, etc
4) Choose an NFT Platform
An ever-growing list of NFT platforms allows you to create an NFT, but the best ones offer a full-service marketplace to list and sell NFTs. Here are a few of the most popular NFT platforms:
OpenSea: The most popular NFT platform by far is OpenSea. With more than $20 billion in trading volume since its launch in 2017 and more than two million NFT collections listed, OpenSea is the top platform for Ethereum-based NFTs.
Solanart: The Solana-based NFT platform Solanart presents top Solana NFT collections as well as offers an easy process for NFT minting alongside its sleek user interface.
Crypto exchanges: NFT creation features exist on multiple crypto exchanges including Binance Exchange.. You are able to generate an NFT directly within the platform while choosing your blockchain preference and minting it instantly.
5) Create the NFT
Once you have chosen a platform, creating an NFT is pretty straightforward. Here is an example for creating an NFT on OpenSea:
Connect your wallet: After you begin signing up for your OpenSeas account you must connect your wallet following a system prompt. You need to sign for verification in your wallet application.
Create a smart contract: To start your new collection on OpenSea Studio choose the “Create” button before selecting “Create a new collection.” The collection process continues by opening a page designed specifically for smart contract creation. Place your media into the page drag area select metadata for your contract and token analyze which blockchain you intend to utilize afterwards proceed by clicking continue. Your wallet will prompt you to sign it when you reach that point.
Create the NFT: After creating your collection an NFT creation screen will display. Click on “Create an NFT.” You determine your NFT title and quantity here while adding details about your project with a description and external link together with additional traits when needed. Users need to upload media either by browsing files or dragging-and-dropping into the designated area before clicking “Create” and completing wallet sign-in.
6) List the NFT for Sale
Selling an NFT through the correct platforms maintains ease because a number of platforms offer free listing services. The creation of your NFT along with adding it to your wallet enables you to select a platform and click a “sell” button to begin the listing process. Set your desired sale price for your NFT followed by defining the duration the listing should remain active.
Once all sale information is provided on the platform you can proceed to create the listing for your item. You need to confirm multiple digital transactions through your wallet together with potential blockchain transaction fee payments. You’ll pay only about $0.01 for Solana transactions yet listing an NFT on Ethereum requires a variable fee which depends on the blockchain’s current network usage.
Blockchain and Fungibility 💵
Cryptocurrencies operate as fungible assets which allow holders to perform trade or exchange transactions between identical units. An exchange lists all bitcoins at equivalent values and also maintains dollar bills at fixed values of $1 each according to U.S. currency standards. The fungible feature which allows for equivalent trading positions cryptocurrencies as secure means for digital economic transactions.
Because NFTs establish both uniqueness and irreplaceability in their tokens creators eliminated any chance of one NFT being equal to any other NFT. Every NFT has distinctive signs similar to digital passports since they serve as digital asset symbols which carry irreplaceable attributes that separate each token from others. NFTs allow creators to combine two distinct digital assets to create a new third NFT which the crypto world refers to as “breeding”.
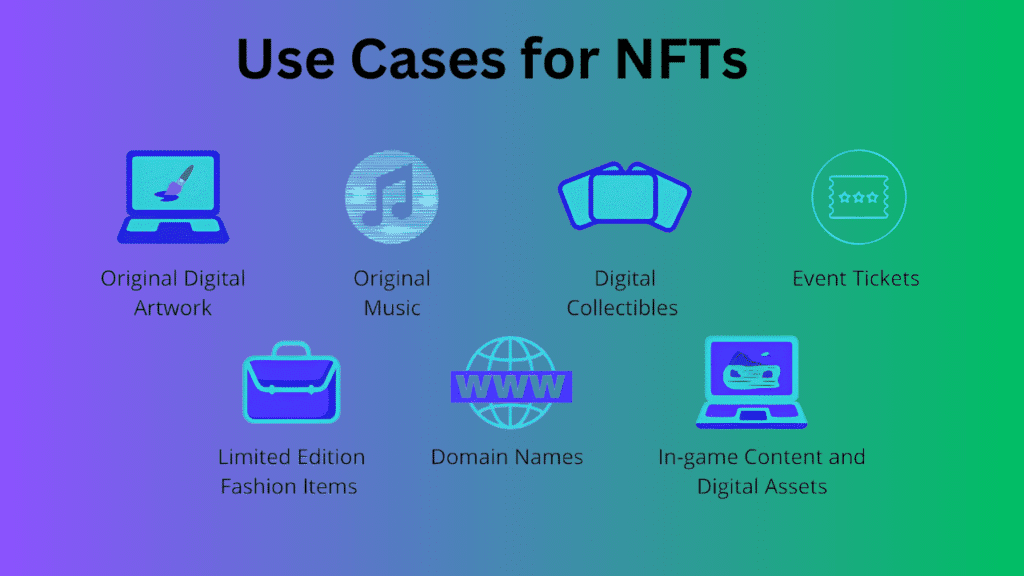
Use Cases for NFTs 🌟
The functionality of NFTs reaches past digital art into multiple sectors which realize benefits from blockchain-based ownership confirmation and scarcity communication. Some key use cases include:
Digital Art and Collectibles: NFT tokens transform the art industry because they enable artists to sell digital certificates of their work which preserve their creativity’s original ownership details alongside rights to receive payments for future sales. Rare virtual items and virtual trading cards stand among digital collectibles that now attract popular attention.
Gaming and Virtual Assets: The gaming sector recognizes NFTs as technology that empowers players with full control over their virtual possessions for ownership and commerce while allowing them to record transactions for game elements ranging from characters to virtual properties. Occasionally these assets enable users to move them across multiple games which helps establish interoperability.
Music and Entertainment: Music industry stakeholders employ NFT technology to distribute exclusive albums and merchandise and secure direct concert ticket sales with their fans. NFTs enable artists to generate ongoing revenue through resale royalties which establish new financial income avenues.
Real Estate and Property Ownership: In real estate investigations NFT technology provides a way to establish digital tokens for both physical and virtual property ownership. The technology permits fractional asset division while creating simplified asset transfer methods paired with clear property documentation.
Fashion and Luxury Goods: Luxury product brands have started using NFT digital technology to provide customers with authenticated and genuine designer bags and other luxury merchandise including watches and sneakers.
Identity and Certification: NFT technology enables secure academic record monitoring since professional licenses and academic credentials receive efficient digital verification without fraud risks.
Sports and Fan Engagement: Through the distribution of NFT-based collectibles plus tickets and exclusive fan experiences sports organizations boost fan interaction while developing fresh revenue streams.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) and Tokenized Assets: NFT-enabled DeFi platforms create possibilities for users to back loans with tokens and take part in both staking processes and governance operations.
NFTs showcase utility beyond digital works of art as they transform industries with their capacity to guarantee ownership while delivering improved security with financial innovation benefits.
The Benefits of NFTs 🌞
Authenticity
NFTs perform their main function as authenticity markers that provide provenance to digital assets. The blockchain establishes the uniqueness of each NFT thereby simplifying how people determine digital asset authenticity. The art world heavily requires solutions because fake pieces and imitation works constitute serious issues. NFT technology lets creators of digital works prove ownership while preventing unauthorized replications and misattribution.
Traceability
NFTs authenticate items while allowing users to monitor previous ownership details about any specific digital asset. Owners of expensive objects such as artworks or collectibles find provenance verification through NFTs critical because ownership records can determine an item’s total worth. NFT platforms enable tracking of ownership details as blockchain records every transaction done with NFT items.
Accessibility
NFTs provide users with full access wherever they need to interact with them. The digital nature of NFTs enables smooth trading procedures as well as worldwide access to the assets. The technology enables artists and collectors from any location worldwide to participate in the art market together. NFTs are available for purchase through fractional shares thereby broadening investment possibilities for more individuals in expensive artworks.
New Revenue Streams
NFT technology delivers fresh avenues of earnings for both artists and creative professionals. Artists generate revenue by producing original digital assets which opens access to a new market opportunity for their art. NFT creators can implement smart contracts into their assets to receive payment shares from every following resale of their work. Artists earn ongoing profit as their NFT assets appreciate in value because they receive from the increasing worth.
Security
The security of identity verification improves when utilizing non-fungible tokens. Private individuals holding encryption keys must access personal data stored on an immutable blockchain system to interact with or exploit the information.
Concerns About Non-Fungible Tokens 🛡️
Prospective investors and individuals who want to mint NFTs must evaluate potential problems despite their possible advantages to creators and various stakeholders.
The ownership functionality of the token combines hashed metadata with corresponding key pairs which are produced by your wallet. Anyone can replicate and share a digitized image or video, music files with other files by using multiple techniques without requiring authorization. Any user may easily duplicate an image by using the right-click feature to save it.
Any person who replicates or distributes a tokenized digital asset engages in asset piracy since ownership rights for this digital asset have been confirmed. Owners face the burden of finding perpetrators to press charges when their multitudes misuse digital assets.
The liquidity of non-fungible tokens is very restricted to possibilities of market trade. Specific audience members of collectors or buyers pursue non-fungible tokens due to their distinct nature which surpasses the broad characteristics of standard cryptocurrencies. Old or forgotten NFT assets often become challenging to sell because their collectors’ interest fades over time.
The Bottom Line 🎯
Despite experiencing diminished popularity numerous collectors and traders remain committed to purchasing NFTs which captivate their interest.
Digital creators the NFTs by understanding minting protocols must interact with blockchain systems through cryptocurrency wallets and transaction marketplaces while managing associated gas fees. People who master NFT operations find launching them straightforward since much of the procedure functions automatically, apart from selecting NFT content.
Non-fungible tokens represent how cryptocurrency concept has developed to its next stage. Today’s financial systems feature advanced trading and loan methods which support a wide variety of assets which include real estate, lending agreements, and pieces of artwork. The ability to represent digital assets enables NFTs to evolve the platform infrastructure.
The concept of digital representation of physical assets exists long before this technology advanced because digital identification provides uniqueness safeguards. All these ideas reveal their full potential for transformation when they operate within a tamper-proof blockchain environment that uses smart contracts and automated processes.
FAQ 💡
What are NFTs, and how do they work?
NFTs, or Non-Fungible Tokens, are unique digital assets stored on a blockchain that represent ownership of a specific item, such as art, music, or collectibles. Unlike cryptocurrencies, NFTs cannot be exchanged on a one-to-one basis due to their uniqueness.
Why are NFTs valuable?
NFTs derive their value from their scarcity, authenticity, and the demand for the digital asset they represent. They allow creators to monetize their work and provide buyers with verifiable ownership of unique digital items.
How do NFTs differ from cryptocurrencies?
While both NFTs and cryptocurrencies use blockchain technology, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are fungible (interchangeable), whereas NFTs are non-fungible, meaning each token is unique and cannot be replaced by another.
What can NFTs be used for?
NFTs are used for a variety of purposes, including digital art, music, virtual real estate, gaming items, and even tokenized real-world assets like real estate or collectibles. They enable creators to sell and authenticate their work digitally.
How do I buy or sell NFTs?
NFTs are bought and sold on specialized marketplaces like OpenSea, Rarible, or Foundation. You’ll need a cryptocurrency wallet, such as MetaMask, and cryptocurrency (usually Ethereum) to purchase or trade NFTs.
Are NFTs environmentally friendly?
NFTs have faced criticism for their environmental impact due to the energy-intensive nature of blockchain networks like Ethereum. However, advancements in blockchain technology, such as Ethereum 2.0, aim to reduce their carbon footprint.
References 🔗
- https://www.coindesk.com/learn/what-are-nfts/
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestechcouncil/2021/03/30/what-are-nfts-and-why-are-they-revolutionizing-the-art-world/
- https://ethereum.org/en/nft/
- https://www.theverge.com/22310188/nft-explainer-what-is-blockchain-crypto-art-faq
- https://opensea.io/blog/guides/nft-marketplace-guide/


