Table of Contents
Digital innovation has exceeded the capabilities of traditional security models in current times. Data breaches caused by authorized insiders account for 82 percent of all incidents. Shocking, right? The security practice that relies on building a secure network perimeter followed by hope for its stability no longer addresses modern sophisticated cyber threats. Zero-Trust Architecture operates as an effective solution to address these security needs.
Zero-Trust is about getting rid of the assumptions of trust. It overrides the old notion of having a trust boundary by neutralizing to the fact that nobody- be it inside or outside the business perimeter has any default access. Every user, device, and access request must constantly go through verification. In short, every process will have to be authenticated. Quite a lot, right? It is! But as we see more and more sophisticated and covert cyber-attacks, the strategy is becoming the standard for modern cybersecurity.
Your organization and you need to understand how these developments affect you. The capability to observe and maintain constant management over your entire network infrastructure exists in real time. The implementation of Zero-Trust Architecture becomes feasible through the deployment of micro-segmentation coupled with least privilege access which blocks external unauthorized users across the network boundaries. Secure data access depends on granting access only to individuals who require the information to carry out their duties.
As organizations migrate to the cloud, embrace IoT, and support remote work, the vulnerabilities in traditional systems grow exponentially. This is why Zero-Trust isn’t just a trend—it’s becoming an essential part of data protection and network security for businesses of all sizes. In this article, we’ll explore how Zero-Trust works, its key benefits, and how adopting this approach can future-proof your organization against the most serious threats in cybersecurity today.
Let’s dive in and see how Zero-Trust Architecture is reshaping the way we think about cyber risk management and online security.
The Rise of Cybersecurity Threats 🌱
It wasn’t long ago that many companies believed their biggest cybersecurity threat was an external hacker trying to breach their firewall. But times have changed. One day, while managing a client’s network security, I realized that the biggest threat wasn’t some distant outsider—it was an insider who had accidentally left a sensitive file open on a public-facing server. A simple mistake, but it cost thousands. And that’s the problem: security breaches often come from the inside, whether due to human error, poor access management, or insufficient monitoring.
Cyber threats today are a lot more insidious and harder to detect than in the past. Ransomware attacks, for instance, are up 150% from just a few years ago. And while everyone’s focused on securing external access points, what about the internal systems? The traditional perimeter defense model simply isn’t cutting it anymore. It’s a bit like trying to guard a castle by fortifying the walls and leaving the backdoor wide open. You need to close every potential entry point.
The truth is, the nature of cyber threats has evolved in a way that challenges legacy systems. There was a time when companies could rely on firewalls and antivirus software to ward off external threats. But as businesses move more of their operations to the cloud and implement hybrid infrastructures, the “castle walls” have become a lot more porous. I’ve seen firsthand how an employee’s outdated password or a vulnerable API can be the weak link in an otherwise strong system. It’s like leaving a key under the doormat for hackers to find.
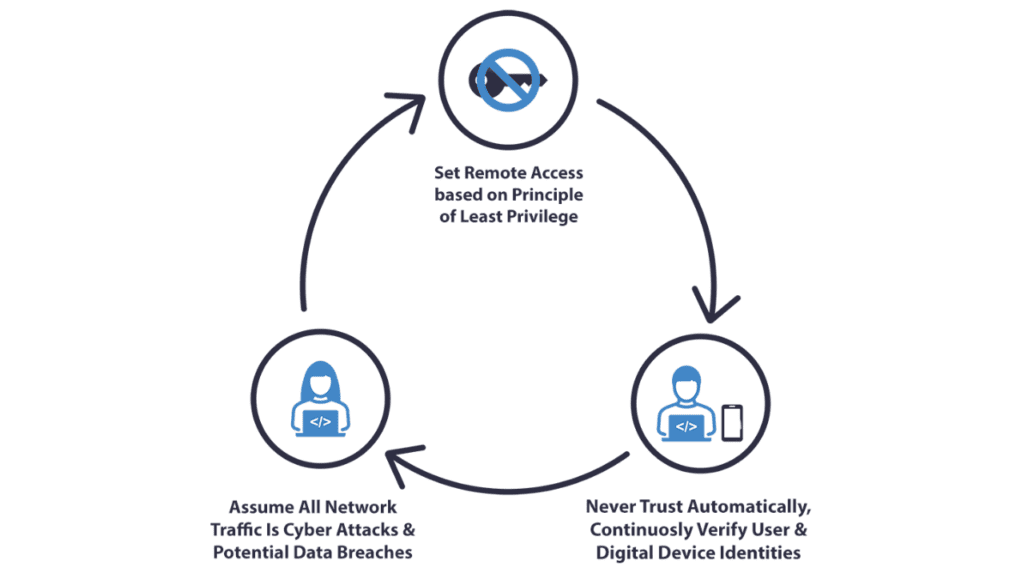
Zero-Trust Architecture (ZTA) is the antidote to this problem. It shifts the focus away from the perimeter and places the emphasis on granular control, continuous verification, and micro-segmentation. Instead of treating everyone inside the network as trustworthy, ZTA forces organizations to constantly authenticate users and devices at every access request. That means no more assuming your internal systems are safe just because they’re behind a corporate firewall.
I’ll be honest, adopting Zero-Trust wasn’t a walk in the park for my team. There were definitely some growing pains—training employees, configuring access management systems, and tweaking network protocols until we got it right. But once we integrated ZTA fully into our security framework, we saw a dramatic reduction in unauthorized access attempts. And the best part? Our systems were far more resilient to phishing and lateral movement—two major tactics often used by attackers to spread malware once they’re inside.
So, here’s a tip: start small with access control policies. Don’t try to overhaul everything at once. Gradually implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) and least-privilege access rules, and work your way up to more sophisticated micro-segmentation. Trust me, it’ll save you a lot of headaches in the long run. Don’t wait until it’s too late. Start questioning every user, every device, and every request—because in the world of cybersecurity, assuming trust is a risky game.
📌 Never Trust, Always Verify
At the heart of Zero-Trust lies one principle: never trust, always verify. It might sound simple, but it’s a radical shift in how organizations approach security. Trusting a user or device just because it’s inside the network is a dangerous assumption. I once worked with a company that had a robust firewall but allowed all devices within their corporate VPN to access sensitive data without further authentication. Then, one day, a hacker found their way through an employee’s compromised credentials. Once in, they moved laterally, accessing files that were meant to be protected. The vulnerability? They trusted the VPN connection too much.
With Zero-Trust, verification happens at every stage. Every time a user tries to access a system or application, they must be re-authenticated. This includes using methods like multi-factor authentication (MFA) and device health checks. Instead of assuming someone is safe just because they’ve logged in once, you’re constantly verifying their credentials, identity, and access permissions. This drastically reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if an attacker has managed to compromise an account.
📌 Micro-Segmentation and Least-Privilege Access
Another critical feature of Zero-Trust is micro-segmentation—dividing a network into smaller, isolated segments to limit the spread of potential breaches. You can think of it as having firewalls within firewalls, where access is tightly controlled and monitored for each segment. It’s a little like having security checkpoints within a building rather than just guarding the front door. If someone gets through one checkpoint, they can’t access the entire building.
I remember when we implemented least-privilege access for a financial services company. Employees could only access the exact data they needed to do their jobs—no more, no less. This prevented a lot of unnecessary risk. If a user’s account was compromised, the attacker could only access the limited data tied to that account, making it much harder for them to escalate their privileges or move around undetected.
Tip: Implementing micro-segmentation takes time. Start with critical systems, then slowly expand as you refine your security processes. Don’t forget to use role-based access controls (RBAC) to make sure only the right people have access to the right data!
📌 Continuous Monitoring and Validation
One of the biggest mistakes I’ve seen in cybersecurity is treating verification as a one-time event. In traditional systems, once a user is authenticated, they’re often granted unrestricted access until they log off. With Zero-Trust, that assumption is thrown out the window. Continuous monitoring is key.
Imagine this: A system is compromised, but instead of waiting until an alert pops up, Zero-Trust systems keep an eye on every transaction. If a user tries to access a file they don’t typically access or uses a device outside of their usual work parameters, the system flags it. This kind of ongoing validation ensures that even if someone bypasses initial security measures, their actions will be tracked in real-time.
From my experience, implementing continuous monitoring can feel overwhelming at first. But once we started using tools like behavioral analytics and anomaly detection, it was a game-changer. We could quickly spot strange activity and lock down systems before any real damage was done. Tip: Use automated systems to monitor user behavior and network traffic. This way, you’ll spot a breach before it snowballs into something worse!
The Role of Zero-Trust in Preventing Cyber Attacks 🛡️
Zero-Trust architecture (ZTA) is a powerful defense against modern cyber threats. It’s designed to stop attacks in their tracks by assuming no one inside or outside the network is trustworthy. Whether the threat comes from insiders, phishing scams, or attackers attempting to move laterally within your systems, Zero-Trust ensures that access is constantly monitored, verified, and restricted to only what’s necessary. Let’s dive into how Zero-Trust actively prevents different types of cyber threats, providing organizations with a dynamic and secure defense.
🔹Reducing Insider Threats
Insider threats can be tricky because they often involve employees or trusted individuals who either act maliciously or have their credentials compromised. Zero-Trust directly addresses this by verifying the identity of both internal and external users at every interaction.
I remember a case where a company experienced a data breach from an employee who had malicious intent. Initially, the breach wasn’t detected because the employee had access to sensitive systems based on their role. But with Zero-Trust, even internal employees aren’t automatically trusted. Every time they access something, their identity is verified using multi-factor authentication (MFA) and least-privilege access policies.
The principle behind this approach is simple but effective: don’t trust anyone, even if they are already inside the network. By continually verifying users, especially when they move across different applications or systems, you significantly reduce the chance of insider threats. The result is that even if an insider’s credentials are compromised, the damage is limited because they don’t have unrestricted access to everything in the network.
🔹Defending Against Phishing and Credential Theft
Phishing and credential theft are two of the most common ways attackers gain access to systems. With Zero-Trust in place, the impact of these types of attacks is drastically minimized.
In my experience, phishing attempts often succeed because users can easily fall for emails or messages that seem legitimate. But in a Zero-Trust system, credentials are just one piece of the puzzle. To access a system, a user must pass multiple layers of verification. For example, even if an attacker manages to steal a password, it’s useless without the second layer of authentication, such as a phone-based authentication code or a biometric check.
Another thing I’ve noticed with Zero-Trust is that it constantly monitors user behavior for anomalies. If someone logs in from an unusual location or tries to access resources outside of their usual scope, the system flags this as suspicious and blocks the access until further verification is provided. This proactive approach makes phishing much less successful because stolen credentials alone won’t guarantee access to sensitive data.
🔹Limiting Lateral Movement and Containment
One of the most dangerous aspects of a cyber attack is the ability for an attacker to move freely through a network once they breach an initial point. This is where Zero-Trust really shines. By using micro-segmentation and enforcing least-privilege access, Zero-Trust prevents attackers from accessing more than what’s necessary.
I recall working with a company that had a solid perimeter defense, but when a hacker gained access to a single user’s credentials, they were able to navigate across multiple systems without much resistance. The breach went unnoticed until significant damage was already done. If they had implemented Zero-Trust, the attacker would have been immediately stopped in their tracks after breaching the first system, thanks to segmented access controls.
Micro-segmentation is the practice of dividing a network into smaller, isolated sections so that if an attacker compromises one area, they cannot automatically move to the rest of the network. Each segment requires separate authentication, which makes it much harder for attackers to spread malware or steal additional data. Along with least-privilege access—giving users only the minimal permissions required for their job—Zero-Trust limits the damage and scope of any breach.
By containing attackers within a small section of the network, Zero-Trust prevents lateral movement. Even if an attacker does get through, they’re restricted to a tiny portion of the infrastructure, which can quickly be isolated and secured. This containment minimizes the damage, reduces recovery time, and prevents full-scale network-wide breaches.
Zero-Trust is transforming cybersecurity by directly addressing the core vulnerabilities in traditional systems. Whether it’s mitigating insider threats, defending against phishing, or limiting lateral movement, Zero-Trust provides the robust, proactive security needed to stay one step ahead of cybercriminals.
How Zero-Trust Architecture Enhances Regulatory Compliance 🌻
When it comes to cybersecurity regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS, compliance is a major concern for businesses. These standards set stringent guidelines to protect sensitive data, and failing to comply can result in hefty fines or reputational damage. Zero-Trust Architecture (ZTA) can make compliance not only easier but more effective. I’ve seen firsthand how implementing ZTA helps organizations stay on top of their compliance game, making it possible to safeguard data and meet regulatory requirements more efficiently.
🔸Streamlining Compliance through Access Controls
One of the key components of Zero-Trust is its access control policies. Instead of assuming that everyone inside your network can access anything they want, ZTA requires continuous authentication. This makes it much easier to comply with regulations like HIPAA, which demand strict control over who has access to sensitive patient data, or GDPR, which requires stringent data access controls to protect the privacy of EU citizens.
I’ve worked with a healthcare provider that struggled with HIPAA compliance before adopting Zero-Trust. Their system was based on trust—once someone was logged in, they had access to a wide array of sensitive patient information. When we switched to a Zero-Trust approach, the organization implemented role-based access control (RBAC), ensuring that only the necessary personnel had access to specific data. This not only reduced the risk of data breaches but also made auditing access a lot easier, as every action was logged and tied to a specific user.
In simple terms: Zero-Trust helps organizations establish a “need-to-know” basis for every piece of sensitive information. If you’re not authorized, you can’t access it—period. This kind of policy doesn’t just make business sense; it’s also a key step in meeting regulatory standards, making compliance a more straightforward process.
🔸Simplifying Auditing and Reporting
One of the biggest headaches I’ve encountered when dealing with regulatory compliance is auditing and reporting. Gathering data, tracking user actions, and generating reports can be a time-consuming task. But Zero-Trust’s continuous monitoring features streamline this entire process, providing organizations with a robust auditing framework.
A few years ago, I worked with a financial institution that had a nightmare during their annual compliance audit. Their old system was based on manual logs, which made it difficult to trace who accessed what and when. With Zero-Trust in place, the company implemented automatic logging of every interaction with sensitive data. These logs were stored securely and could be retrieved instantly for auditing purposes.
What I’ve learned through experience is that Zero-Trust doesn’t just give you the security you need—it gives you the visibility you need for compliance. With continuous monitoring and automated logging, businesses can generate detailed reports for compliance audits in minutes instead of days. For instance, if auditors want to know who accessed a specific file, you can provide them with an audit trail that shows the exact time, the user’s identity, and what action was taken. This simplifies compliance reporting and ensures that everything is documented properly.
In short, Zero-Trust makes regulatory compliance not only achievable but much more manageable. It takes care of the heavy lifting, allowing organizations to focus on their core business activities while still adhering to complex regulations.
Future Trends: The Expanding Role of Zero-Trust Architecture 🛫
Zero-Trust Architecture (ZTA) isn’t just the present; it’s the future of cybersecurity. As organizations embrace emerging technologies like cloud computing and the Internet of Things (IoT), Zero-Trust will become a foundational pillar for securing these complex environments. The increasing adoption of ZTA is a clear signal that traditional security models are no longer enough to protect against modern cyber threats.
◾The Growth of Cloud Security and ZTA
With businesses moving to hybrid and multi-cloud environments, securing cloud infrastructure is more critical than ever. I’ve seen firsthand how companies struggle to implement traditional perimeter-based security when their systems are spread across various cloud platforms. Zero-Trust is the perfect fit here because it doesn’t rely on a perimeter. Instead, it ensures that access is granted based on strict authentication and authorization for each user, device, and service—regardless of where they are in the cloud.
As more businesses shift to the cloud, adopting Zero-Trust will become essential. In my experience, organizations that don’t implement ZTA risk exposing sensitive data and resources. Zero-Trust’s approach helps ensure that the cloud remains secure, even as companies scale or shift to multi-cloud solutions.
◾Zero-Trust in the Internet of Things (IoT) Era
The IoT explosion is already underway, with millions of devices connecting to networks every day. Securing these devices will be a nightmare without the right frameworks. Zero-Trust comes into play by enforcing strong identity verification for each device and user interacting with the network.
I once worked with a company that had an IoT-driven smart factory. They were facing serious security concerns because unauthorized devices were gaining access to critical systems. By implementing Zero-Trust, we established strict identity checks and access policies for each IoT device, ensuring that only authorized devices could communicate with the network. This is crucial as IoT continues to grow, where even a small security lapse could have devastating consequences. Zero-Trust is key to keeping these devices safe in the future.
Conclusion 🎯
The digital-first world demands a cybersecurity evolution which Zero-Trust Architecture successfully leads. ZTA verifies all users together with their devices and connections so it effectively minimizes risks of cyberattacks as well as insider threats and data breaches. The necessity of Zero-Trust Architecture will expand in the future since it enables smooth regulatory compliance and provides security for IoT devices.
ZTA should not be considered as a universal answer. Each organization has exclusive characteristics which affect their challenges and security needs and their specific priorities. Zero-Trust delivers adaptability since organizations can customize it to meet their unique needs. All organizations from small businesses to large enterprise networks can implement ZTA with modifications to match their existing infrastructure. A proper implementation will generate long-term value because this solution needs dedicated setup although it is not a simple one-click method.
A proactive adaptive approach stands as the only effective method to stay ahead of the permanent changes in the digital realm. Zero-Trust represents an organizational approach that brings readiness and preparedness to every situation. Affixed with lessons from this article start creating Zero-Trust architecture structures for your organization immediately. Verification has now replaced trust as our essential practice.
FAQ 💡
What is Zero-Trust Architecture in Cybersecurity?
Zero-Trust Architecture is a cybersecurity framework that operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” Unlike traditional security models that assume trust within a network, the Zero-Trust model requires continuous verification of users, devices, and applications, regardless of their location. This approach minimizes the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access, making it a cornerstone of modern cybersecurity strategies.
Why is Zero-Trust Architecture important for modern cybersecurity?
With the rise of remote work, cloud computing, and increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks, traditional perimeter-based security models are no longer sufficient. Zero-Trust Architecture is critical because it provides enhanced protection against insider threats, phishing attacks, and lateral movement within networks. By adopting a Zero-Trust approach, organizations can ensure robust data security and adapt to the evolving challenges of modern cybersecurity.
How does Zero-Trust Architecture improve data security?
Zero-Trust Architecture improves data security by enforcing strict access controls, implementing micro-segmentation, and encrypting data at every stage. By verifying every user and device before granting access, it ensures that sensitive information is only accessible to authorized entities. This least privilege access approach significantly reduces the risk of data leaks and cyberattacks, making it a vital component of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy.
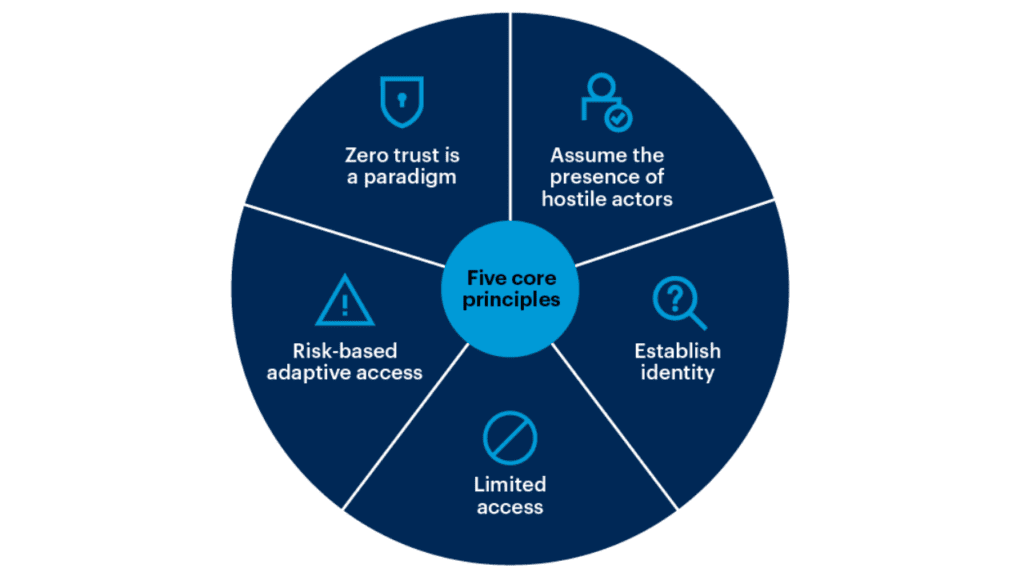
What are the key principles of Zero-Trust Architecture?
The key principles of Zero-Trust Architecture include:
Least Privilege Access: Granting users the minimum access necessary to perform their tasks.
Continuous Verification: Authenticating and authorizing users and devices at every step.
Micro-Segmentation: Dividing networks into smaller zones to limit lateral movement.
Assume Breach: Operating under the assumption that threats exist both inside and outside the network.
These Zero-Trust principles form the foundation of a robust cybersecurity framework that prioritizes data protection and risk mitigation.
How does Zero-Trust Architecture support remote work and cloud security?
Zero-Trust Architecture is ideal for remote work and cloud security because it doesn’t rely on a fixed network perimeter. Instead, it secures access to cloud-based applications and data by continuously verifying users and devices, regardless of their location. This ensures that remote employees can work securely without compromising organizational data. By integrating Zero-Trust principles, businesses can protect sensitive information in hybrid work environments and maintain a strong cybersecurity posture.
What are the challenges of implementing Zero-Trust Architecture?
Implementing Zero-Trust Architecture can be challenging due to factors like:
Complexity: Requires a complete overhaul of existing security infrastructure.
Cost: Significant investment in tools, training, and resources for Zero-Trust adoption.
User Experience: Balancing secure access with seamless usability for employees.
Despite these challenges, the long-term benefits of enhanced data security, reduced cyberattack risks, and improved compliance make Zero-Trust Architecture a worthwhile investment for organizations looking to future-proof their cybersecurity strategies.